PYRAZINAMIDE
DOSAGE
Adults (<50kg): 1.5g once a day (oral); or for DOT supervised regimen: 2g three times a week (oral).
Adults (50kg+): 2g once a day (oral); or for DOT supervised regimen: 2.5g three times a week (oral).
Children: 30-40mg/kg once daily (max. 1.5g if <50kg; 2g if 50kg+) once a day (oral); or for DOT supervised regimen: 50mg/kg (max. 2g if <50kg; 2.5g of 50kg+) three times a week (oral). (Doses should be rounded up to facilitate administration of suitable volumes of liquid or an appropriate strength of tablet)
Pyrazinamide may be taken with or without food.
PREPARATIONS
Oral: 500mg tablets.
Liquid (as a manufactured ‘special’ - unlicensed medicine).
Rifater tablets (rifampicin 120mg, isoniazid 50mg, pyrazinamide 300mg).
Voractiv® tablets (rifampicin 150mg, isoniazid 75mg, pyrazinamide 400mg, ethambutol 275mg).
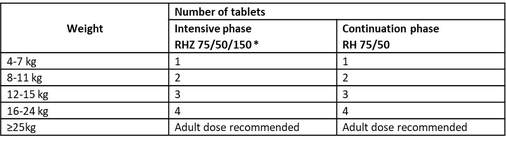
Paediatric oral fixed dose combinations (dissolvable in water):
*Ethambutol should be added in the intensive phase for children with extensive disease or living in settings where the prevalence of HIV or of isoniazid resistance is high.
DRUG LEVEL MONITORING
Indications for monitoring:
Timing of sample:
ADVERSE EFFECTS
COMMON:
Hyperuricaemia.
Arthralgia.
Gastrointestinal: Anorexia, nausea, vomiting.
Hepatic: Transient increases in LFTs.
Dermatological: Rash.
SERIOUS:
Haematological: Sideroblastic anaemia (rare), thrombocytopaenia (rare).
Hepatotoxity.
ADVERSE EFFECTS: MONITORING
Routine tests as per generic MDR-TB treatment monitoring guidelines.
INTERACTONS
Probenecid: Pyrazinamide antagonises the effect of probenecid.
Sulfinpyrazone: Pyrazinamide antagonises the effect of sulfinpyrazone.
This information is not inclusive of all drug interactions. Please discuss with a pharmacist.
CONTRA-INDICATIONS & CAUTIONS
Contraindications:
Hypersensitivity: To pyrazinamide.
Cautions:
Gout.
Liver Disease.
LABORATORY INFORMATION
Please find up to date information at www.assayfinder.com regarding individual providers of drug level monitoring tests. Click on the provider to discover contact details. Turnaround time varies depending on the test and whether it is run locally or sent to an external lab. By contacting laboratories in advance, turnaround time can significantly be reduced.
Sample Type: Serum.
Volume Required: 2 ml.
Sample Container: Plain (non SST).
Container Type: Any.
Availability: Office Hours.
Turnaround Time: 7 Days.
Adults (<50kg): 1.5g once a day (oral); or for DOT supervised regimen: 2g three times a week (oral).
Adults (50kg+): 2g once a day (oral); or for DOT supervised regimen: 2.5g three times a week (oral).
Children: 30-40mg/kg once daily (max. 1.5g if <50kg; 2g if 50kg+) once a day (oral); or for DOT supervised regimen: 50mg/kg (max. 2g if <50kg; 2.5g of 50kg+) three times a week (oral). (Doses should be rounded up to facilitate administration of suitable volumes of liquid or an appropriate strength of tablet)
Pyrazinamide may be taken with or without food.
PREPARATIONS
Oral: 500mg tablets.
Liquid (as a manufactured ‘special’ - unlicensed medicine).
Rifater tablets (rifampicin 120mg, isoniazid 50mg, pyrazinamide 300mg).
Voractiv® tablets (rifampicin 150mg, isoniazid 75mg, pyrazinamide 400mg, ethambutol 275mg).
Paediatric oral fixed dose combinations (dissolvable in water):
*Ethambutol should be added in the intensive phase for children with extensive disease or living in settings where the prevalence of HIV or of isoniazid resistance is high.
DRUG LEVEL MONITORING
Indications for monitoring:
- Known or suspected malabsorption.
- Poor treatment response.
Timing of sample:
- 2 hours post dose.
- Repeat at 6 hours if suspect delayed.
- Drug levels need not be routinely measured.
ADVERSE EFFECTS
COMMON:
Hyperuricaemia.
Arthralgia.
Gastrointestinal: Anorexia, nausea, vomiting.
Hepatic: Transient increases in LFTs.
Dermatological: Rash.
SERIOUS:
Haematological: Sideroblastic anaemia (rare), thrombocytopaenia (rare).
Hepatotoxity.
ADVERSE EFFECTS: MONITORING
Routine tests as per generic MDR-TB treatment monitoring guidelines.
INTERACTONS
Probenecid: Pyrazinamide antagonises the effect of probenecid.
Sulfinpyrazone: Pyrazinamide antagonises the effect of sulfinpyrazone.
This information is not inclusive of all drug interactions. Please discuss with a pharmacist.
CONTRA-INDICATIONS & CAUTIONS
Contraindications:
Hypersensitivity: To pyrazinamide.
Cautions:
Gout.
Liver Disease.
LABORATORY INFORMATION
Please find up to date information at www.assayfinder.com regarding individual providers of drug level monitoring tests. Click on the provider to discover contact details. Turnaround time varies depending on the test and whether it is run locally or sent to an external lab. By contacting laboratories in advance, turnaround time can significantly be reduced.
Sample Type: Serum.
Volume Required: 2 ml.
Sample Container: Plain (non SST).
Container Type: Any.
Availability: Office Hours.
Turnaround Time: 7 Days.