BEDAQUILINE
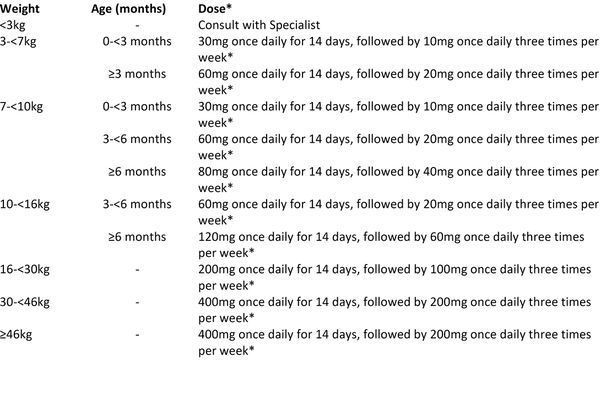
DOSAGE
Adults (aged 18 to 64 years): 400 mg daily for the first 2 weeks, followed by 200 mg three times per week for the remaining 22 weeks. (Maximum duration = 6 months).
Children:
When available, bedaquiline 20mg dispersible tablets should be prioritised for young children over the adult 100mg formulation. Alternatively, Bedaquiline 100mg tablets can be crushed and suspended in water, and have been shown to be bioequivalent to tablets swallowed whole.
Bedaquiline should be taken with food.
Patients should be advised to avoid alcohol whilst on bedaquiline.
PREPARATIONS
Oral: 100mg tablets, 20mg dispersible tablets
DRUG LEVEL MONITORING
- Drug levels need not be routinely measured.
ADVERSE EFFECTS
•Report all suspected adverse drug reactions to the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) through the Yellow Card Scheme.
COMMON:
Arthralgia
Chest pain
Gastrointestinal: Nausea.
Neurological: Headache.
Respiratory: Haemoptysis
SERIOUS:
Cardiovascular: QTc prolongation (more common in hypokalaemia, proarrhythmic conditions, in combination with other drugs that prolong the QT interval such as clofazimine, fluoroquinolones or macrolides).
Hepatic: Increases in LFTs.
ADVERSE EFFECTS: MONITORING
ECG: Baseline, 2 weeks then every month and after the addition of any new medication that is known to prolong QT.
•Discontinue bedaquiline and all other QT prolonging drugs if the patient develops:
- Clinically significant ventricular arrhythmia
- A QTc interval of > 500 ms (confirmed by repeat ECG)
- Monitor ECGs frequently to confirm that the QTc interval has returned to baseline.
- If syncope occurs, obtain an ECG to detect QT prolongation.
U&Es, calcium & magnesium: at baseline and repeated monthly and if QT prolongation is detected.
Routine tests as per generic MDR-TB treatment monitoring guidelines.
INTERACTIONS
Anti-arrhythmics: Risk of prolonged QT interval (e.g. amiodarone, sotalol, procainamide, dysopyramide and quinidine).
Antiretrovirals: Limited data.
Antidepressants, Tricylic: Risk of prolonged QT interval.
Antipsychotics (thioridazine, haloperidol, chlorpromazine, trifluoperazine, percycline, prochlorperazine, fluphenazine, sertindole, and pimozide): Risk of prolonged QT interval.
Azole antifungals (e.g. ketoconazole, voriconazole, itraconazole, fluconazole): Increased exposure to bedaquiline. Avoid co-administration for more than 14 days.
Carbamazepine: Accelerated metabolism of bedaquiline resulting in reduced effect. Avoid co-administration.
Chloroquine & hydroxychloroquine: Risk of prolonged QT interval.
Clofazimine: Risk of prolonged QT interval.
CYP3A4 inducers: Accelerated metabolism of bedaquiline resulting in reduced effect. Avoid co-administration.
CYP3A4 inhibitors: Reduced metabolism resulting in increased serum concentrations of bedaquiline. Avoid prolonged co-administration for more than 14 days.
Fluoroquinolones: Risk of prolonged QT interval.
Macrolides: Risk of prolonged QT interval. Avoid co-administration for more than 14 days.
Phenytoin: accelerated metabolism of bedaquiline resulting in reduced effect. Avoid co-administration.
Rifampicin, Rifabutin & Rifapentine: accelerated metabolism of bedaquiline resulting in reduced effect. Avoid co-administration.
Statins: Avoid co-administration.
This information is not inclusive of all drug interactions. Please refer to the SPC or BNF for further information, or discuss with a pharmacist.
CONTRA-INDICATIONS & CAUTIONS
Contraindications:
Hypersensitivity: To bedaquiline.
Children aged <18 years: The safety and effectiveness has not been established in children.
Cautions:
Elderly patients ≥ 65 years: Lack of data in patients aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients.
Pregnancy: Limited data in humans. Animal data suggests low risk. Consider using if the benefits of treatment outweigh the risks of not treating.
Breastfeeding: No data. Expected to be excreted into the breast milk, but high plasma protein binding may reduce the amount excreted. Systemic exposure in breastfed infants may be similar to the breastfeeding mothers. Manufacturer recommends avoiding breastfeeding.
Extrapulmonary TB (e.g. meningitis): There are no data on the use of bedaquiline in extra pulmonary TB and consequently it is not currently recommended for the treatment of this.
Cardiovascular: Due to the risk of QT prolongation with bedaquiline, ECGs should be monitored closely in patients:
- Taking other QT prolonging drugs (e.g fluoroquinolones, macrolides, clofazimine).
•With serum calcium, magnesium, or potassium levels below the lower limits of normal.
HIV/TB co-infection: limited or no information on the use of bedaquiline.
Alcohol or substance use: Limited or no information on alcohol or substance use in association with bedaquiline however, manufacturer recommends avoiding alcohol whilst taking bedaquiline.
Liver disease: Lack of data in severe liver disease. No dose adjustment required in mild to moderate hepatic impairment.
Renal disease: Use with caution in patients with severe renal impairment or end stage renal disease requiring hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis.
LABORATORY INFORMATION
Please find up to date information at www.assayfinder.com regarding individual providers of drug level monitoring tests. Click on the provider for contact details. Turnaround time is usually a few days to a week but this can be reduced by calling ahead and informing the laboratory in advance.